Which Best Describes the Structure of Most Potassium Channels
This architecture also describes the pore of cyclic nucleotidegated channels and probably Na and Ca 2 channels as well. The structure shown here from PDB entry 1bl8 shows the filter portion of a bacterial potassium channel.

Nervous System Questions W Pics Flashcards Quizlet
At the peak action potential K channels open and the cell becomes c hyperpolarized.

. Channels are closed at physiological ATP concentrations but open as the ATPADP ratio decreases during hypoxia or. Repolarization follows with an efflux of potassium through fast potassium channels in phase 1 calcium influx in phase 2 and efflux of potassium through delayed potassium channels in phase 3. The most familiar potassium channel subunits additionally contain either six Shaker-like or two inward-rectifier type transmembrane segments Figure 1.
P loops mediate ion selectivity. Since the first atomic structure of a prokaryotic potassium channel KcsA a channel from Streptomyces lividans was determined tremendous progress has been made in understanding the mechanism of potassium channels and channels conducting other ions. A variety of two P domain subunits has also been described.
Which of the following statements regarding the structure of the voltage-gated Na channels is false. A potassium ions can only flow outside the neurons. D When potassium channels open the membrane potential of the cell moves towards -90 mV.
In this review we discuss the structure of various kinds of potassium channels including the. Whenever an atom gains or loses one or more electrons it converts into either a positive or negative charge which are termed as ions. Perhaps the best-known case is the regulation of the inwardly.
The potassium channel from Streptomyces lividans is an integral membrane protein with sequence similarity to all known K channels particularly in the pore region. BWhen a potassium channel is opened potassium enters the cell because there is more potassium outside the cell than inside. Additionally at rest more potassium non-gated ion channels emphasized by green circles are open than sodium channels emphasized by the blue circle.
Shaker-type potassium channels remain functional when most of the N-terminal domain is removed. What is it also known as. I The pore is constructed of an inverted teepee with the selectivity filter held at its wide end.
The structure of a potassium channel. It has 4 domains with extensive sequence homology. These channels are typically composed of two parts.
D the voltage-dependent potassium channels cannot be opened. E there are too many sodium ions inside the cell to permit another action potential. This material can be found in a cell membrane.
A reentrant loop the P loop from each subunit contributes to the selectivity filter. The N-terminal domain includes a so-called tetramerization or T1 domain. An important characteristic for an ion channel is its selectivity for a particular ion.
The cell structure found in all cells forms a boundary between a cell and the outside environment and controls. We propose that the following principles underlie the structure and operation of K channels. These organelles are found in plant cells and not in animal cells.
C the voltage-dependent sodium channels cannot be opened. The striped green channels represent potassium leak channels. 1 single-channel recording techniques which have permitted the measurement of currents from individual ion channels in a variety of tissues and 2 molecular cloning which.
The atomic structure of a bacterial homolog the potassium channel KcsA is much smaller than Shaker. What best describes the bromide ion that forms. OUR knowledge of the physiology of ion channels has increased tremendously during the past 15 years largely because of two major technical advances.
The solid yellow channels represent chloride leak channels. In K channels the exquisite selectivity for K over smaller ions especially Na is crucial for physiological functionAs a result identification of the mechanisms of K channel selectivity has been the focus of decades of ion channel research 1 7. This organelle will carry out photosynthesis that converts solar energy into food.
The a resting membrane potential is a result of different concentrations of Na and K ions inside and outside the cell. X-ray analysis with data to 32 angstroms reveals that four identical subunits create an inverted teepee or cone cradling the selectivity filter of the pore in its outer end. Molecular basis of K.
A nerve impulse causes Na to enter the cell resulting in b depolarization. The structure of the bacterial potassium channel KcsA has provided a framework for understanding the related voltage-gated potassium channels Kv channels that are used for signalling in neurons. B autoreceptors are inhibiting the opening of ionotropic sodium channels.
Ionic Bond Bromide ion with 36 electrons and unit negative charge Explanation. We describe here a modularly tunable molecular strategy for construction and combinatorial optimization of highly efficient K -selective channelsIn our strategy a highly robust supramolecular H-bonded 1D ensemble was used to order the appended crown ethers in such a way that they roughly stack on top of each other to form a channel for facilitated ion transport. Potassium atom has atomic number 19 which means it has 19 electrons and 19 protons.
Where does the C-term TM Helix of the K Channel face. The potassium channel from Streptomyces lividans is an integral membrane protein with sequence similarity to all known K channels particularly in the pore region. Segment 4 of each domain is the voltage sensor.
It does not have a voltage sensor and other important domains like the N-terminal tetramerization T1 domain. The channel protein changes its primary structure in response to membrane depolarization. The structure of these additional elements has to be studied in the more complex voltage-gated channels.
K ATP channels are inhibited by ATP which binds to K ir 6 subunits and activated by Mg 2-ADP which binds to the SUR subunits. K ATP channels are composed of four pore-forming K ir 6 α-subunits plus four regulatory sulfonylurea receptor SUR subunits. The filter which selects and allows potassium but not sodium to pass and the gate which opens and closes the channel based on environmental signals.
The structure of the channel pore formed by segments S5 S6 and P is now known in atomic detail from the structure of the largely homologous bacterial KcsA channel. Phase 0 is when rapid depolarization happens due to an influx of sodium ions into the cell. X-ray analysis with data to 32.
The dotted blue channels represent sodium leak channels. Potassium channel blockers typically affect phase 3. What is the structure of the Potassium Ion Channel-Homotetrameric-Folding of the helices forms a filter in the middle of the channel allowing for an ion to coordinate itself to form an ion pore.
Ii The narrow selectivity filter is only 12 Å long. When the membrane is at rest K ions. C When a potassium channel is opened potassium leaves the cell because there is more potassium inside the cell than outside.

Anatomy Ch 9 11 Test Flashcards Quizlet
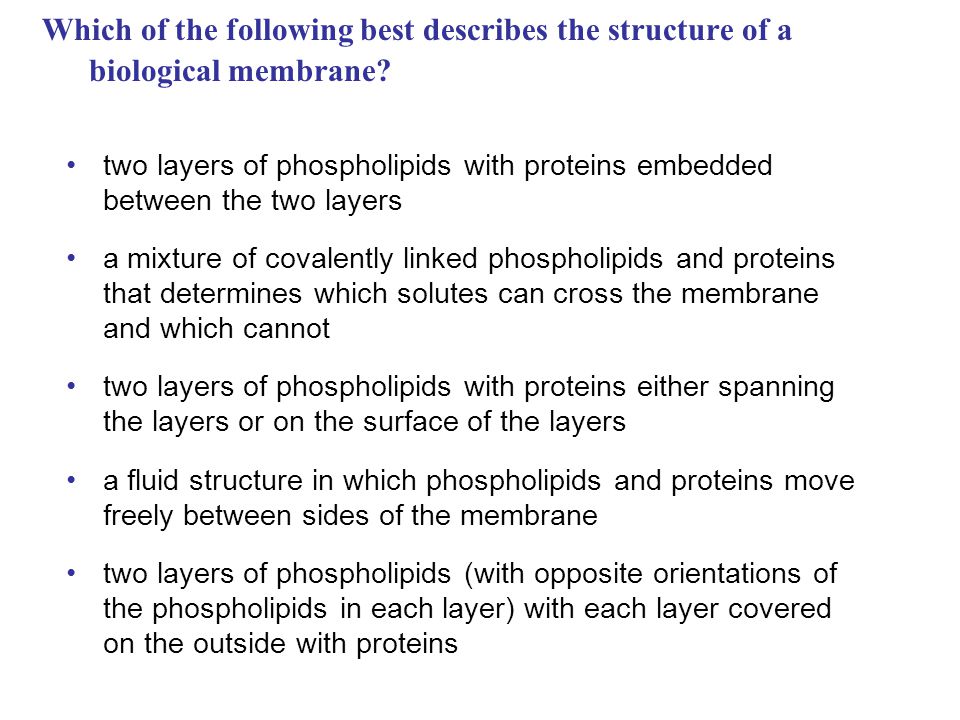
Life At The Edge The Plasma Membrane Is The Boundary That Separates The Living Cell From Its Nonliving Surroundings The Plasma Membrane Exhibits Selective Ppt Download

Chapter 12 Neurons Flashcards Quizlet

9 The Nervous System Flashcards Quizlet

Biochapter7notes 151125141750 Lva1 App6892
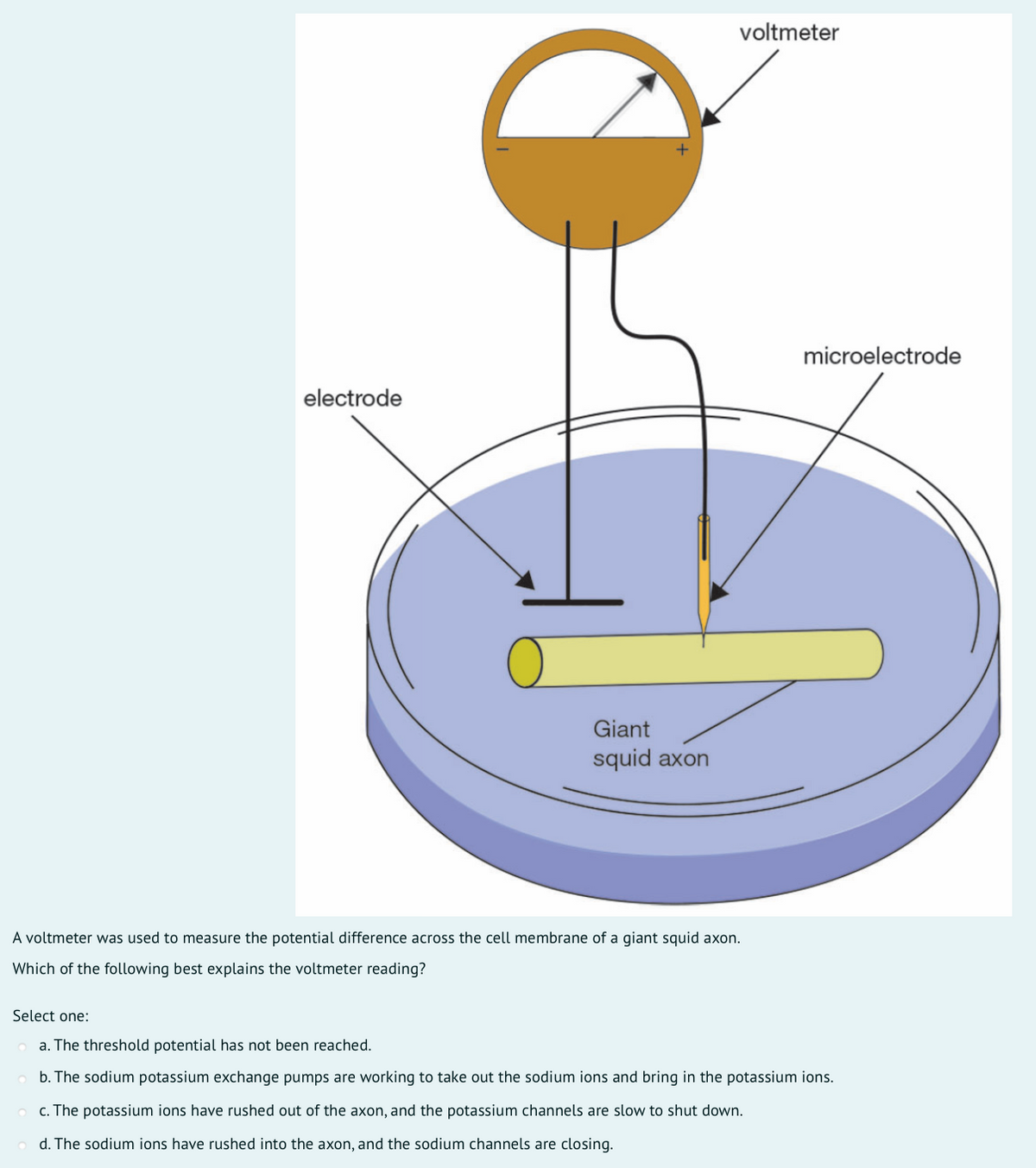
Answered Voltmeter Microelectrode Electrode Bartleby

5 Membrane Transport And Cell Signaling Ppt Download

Chapter 7 Membrane Stucture And Function Ppt Video Online Download

Membrane Transport And Cell Signaling Ppt Download
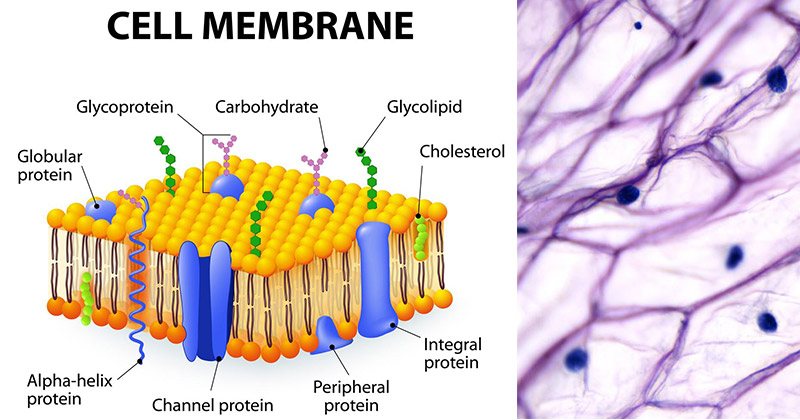
Plasma Membrane Hchs Quiz Quizizz

Pdf The Structure Of The Potassium Channel Molecular Basis Of K Conduction And Selectivity

A P 1 Final Exam Bsc2085 Flashcards Quizlet
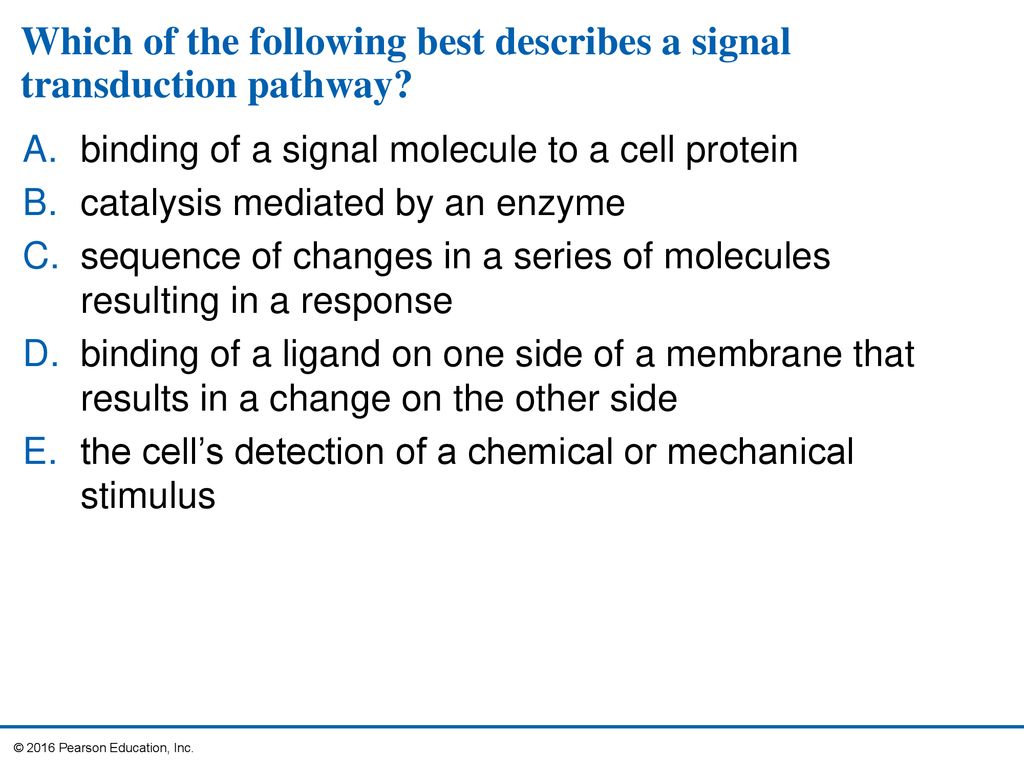
5 Membrane Transport And Cell Signaling Ppt Download

Chapter 11 Homework Flashcards Quizlet

Voltage Gated Potassium Channel An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Ch 11 The Nervous System Flashcards Quizlet

Ap Biology Semester 1 Final Review Flashcards Quizlet


Comments
Post a Comment